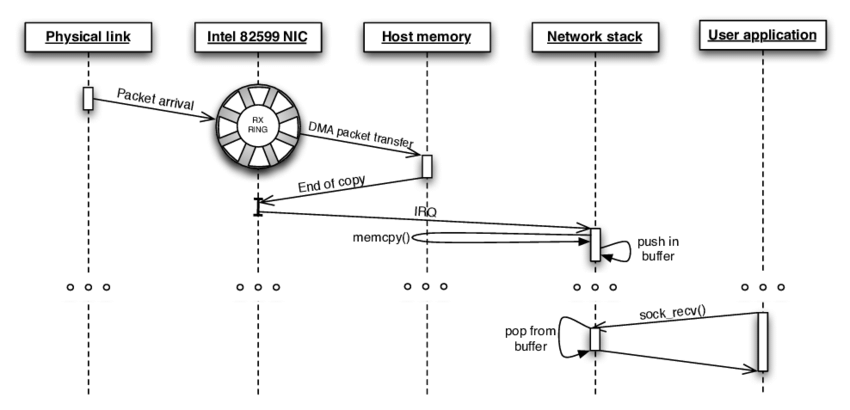
NAPI(New API) 是Linux内核针对网络数据传输做出的一个优化措施,其目的是在高负载的大数据传输时,网络驱动收到硬件中断后,通过poll(轮询)方式将传输过来的数据包统一处理, 在poll时通过禁止网络设备中断以减少硬件中断数量(Interrupt Mitigation),从而实现更高的数据传输速率。
基于NAPI接口, 一般的网络传输(接收)有如下几个步骤:
网络设备驱动加载与初始化(配置IP等)
数据包从网络侧发送到网卡(Network Interface Controller, NIC)
通过DMA(Direct Memory Access) ,将数据从网卡拷贝到内存的环形缓冲区(ring buffer)
数据从网卡拷贝到内存后, NIC产生硬件中断告知内核有新的数据包达到
内核收到中断后, 调用相应中断处理函数, 此时就会调用NAPI接口__napi_schedule开启poll线程(实际是触发一个软中断NET_RX_SOFTIRQ)(常规数据传输, 一般在处理NIC的中断时调用netif_rx_action处理网卡队列的数据)
ksoftirqd(每个CPU上都会启动一个软中断处理线程)收到软中断后被唤醒, 然后执行函数net_rx_action, 这个函数负责调用NAPI的poll接口来获取内存环形缓冲区的数据包解除网卡ring buffer中的DMA内存映射(unmapped), 数据由CPU负责处理, netif_receive_skb传递回内核协议栈
如果内核支持数据包定向分发(packet steering)或者NIC本身支持多个接收队列的话, 从网卡过来的数据会在不同的CPU之间进行均衡, 这样可以获得更高的网络速率
网络协议栈处理数据包,并将其发送到对应应用的socket接收缓冲区
下面就结合具体的代码来看看数据是如何一步步接收的(以intel的千兆以太网卡kernel/drivers/net/intel/e1000为例)。
驱动加载与设备初始化 看e1000_main.c代码,驱动的初始化首先要做的是注册一个pci设备驱动到内核,这样系统启动时会根据PCI的ID列表匹配到该网卡, 并执行设备枚举:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 static int __init e1000_init_module (void ) { int ret; pr_info("%s - version %s\n" , e1000_driver_string, e1000_driver_version); pr_info("%s\n" , e1000_copyright); ret = pci_register_driver(&e1000_driver); ... return ret; } module_init(e1000_init_module); static struct pci_driver e1000_driver = .name = e1000_driver_name, .id_table = e1000_pci_tbl, .probe = e1000_probe, .remove = e1000_remove, #ifdef CONFIG_PM .suspend = e1000_suspend, .resume = e1000_resume, #endif .shutdown = e1000_shutdown, .err_handler = &e1000_err_handler };
匹配到网卡后, pci总线会调用驱动的probe函数, 大致会做如下几个事情:
调用alloc_etherdev 分配一个网络设备对象,并注册到系统中
通过netif_napi_add添加NAPI的poll接口
设置网卡寄存器IO映射内存区域, 用于配置网卡
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 static int e1000_probe (struct pci_dev *pdev, const struct pci_device_id *ent) { .... err = pci_request_selected_regions(pdev, bars, e1000_driver_name); if (err) goto err_pci_reg; pci_set_master(pdev); err = pci_save_state(pdev); if (err) goto err_alloc_etherdev; err = -ENOMEM; netdev = alloc_etherdev(sizeof (struct e1000_adapter)); if (!netdev) goto err_alloc_etherdev; SET_NETDEV_DEV(netdev, &pdev->dev); pci_set_drvdata(pdev, netdev); adapter = netdev_priv(netdev); adapter->netdev = netdev; adapter->pdev = pdev; adapter->msg_enable = netif_msg_init(debug, DEFAULT_MSG_ENABLE); adapter->bars = bars; adapter->need_ioport = need_ioport; hw = &adapter->hw; hw->back = adapter; err = -EIO; hw->hw_addr = pci_ioremap_bar(pdev, BAR_0); if (!hw->hw_addr) goto err_ioremap; if (adapter->need_ioport) { for (i = BAR_1; i <= BAR_5; i++) { if (pci_resource_len(pdev, i) == 0 ) continue ; if (pci_resource_flags(pdev, i) & IORESOURCE_IO) { hw->io_base = pci_resource_start(pdev, i); break ; } } } err = e1000_init_hw_struct(adapter, hw); if (err) goto err_sw_init; ... netdev->netdev_ops = &e1000_netdev_ops; e1000_set_ethtool_ops(netdev); netdev->watchdog_timeo = 5 * HZ; netif_napi_add(netdev, &adapter->napi, e1000_clean, 64 ); strncpy (netdev->name, pci_name(pdev), sizeof (netdev->name) - 1 ); adapter->bd_number = cards_found; err = e1000_sw_init(adapter); if (err) goto err_sw_init; ... if (!is_valid_ether_addr(netdev->dev_addr)) e_err(probe, "Invalid MAC Address\n" ); INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&adapter->watchdog_task, e1000_watchdog); INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&adapter->fifo_stall_task, e1000_82547_tx_fifo_stall_task); INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&adapter->phy_info_task, e1000_update_phy_info_task); INIT_WORK(&adapter->reset_task, e1000_reset_task); ... adapter->wol = adapter->eeprom_wol; device_set_wakeup_enable(&adapter->pdev->dev, adapter->wol); if (hw->mac_type == e1000_ce4100) { for (i = 0 ; i < 32 ; i++) { hw->phy_addr = i; e1000_read_phy_reg(hw, PHY_ID2, &tmp); if (tmp == 0 || tmp == 0xFF ) { if (i == 31 ) goto err_eeprom; continue ; } else break ; } } e1000_reset(adapter); strcpy (netdev->name, "eth%d" ); err = register_netdev(netdev); if (err) goto err_register; ... netif_carrier_off(netdev); e_info(probe, "Intel(R) PRO/1000 Network Connection\n" ); cards_found++; return 0 ; ... }
到这一步网卡还不是可用状态,需要通过用户配置网卡(开启网卡以及配置IP), 如ifconfig eth0 up/ifconfig eth0 <ip>. 设置网卡为UP时,会调用驱动的ndo_open函数:
请求硬件中断,并使能该中断
napi_enable开启napi启动网络的发送队列,允许发送数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 static int e1000_open (struct net_device *netdev) { struct e1000_adapter *adapter = struct e1000_hw *hw = int err; netif_carrier_off(netdev); err = e1000_setup_all_tx_resources(adapter); err = e1000_setup_all_rx_resources(adapter); e1000_power_up_phy(adapter); ... err = e1000_request_irq(adapter); clear_bit(__E1000_DOWN, &adapter->flags); napi_enable(&adapter->napi); e1000_irq_enable(adapter); netif_start_queue(netdev); ew32(ICS, E1000_ICS_LSC); return E1000_SUCCESS; ... return err; }
到此时网卡正常工作, 可以开始接发数据, 我们可以通过ifconfig ethX来查看当前网卡的状态. 接下来, 再来看看数据接收的具体流程。
网卡数据接收 网卡数据的接收大概有三个步骤:
网卡发送中断给驱动
驱动处理函数处理中断,并启动一个napi处理任务
发送接收数据的软中断NET_RX_SOFTIRQ
内核线程处理网络软中断,将数据包发送给上层协议栈
处理网卡中断 在网卡驱动初始化的过程,我们看到驱动会向内核请求中断, 并注册一个中断处理函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 static int e1000_request_irq (struct e1000_adapter *adapter) { struct net_device *netdev = irq_handler_t handler = e1000_intr; int irq_flags = IRQF_SHARED; err = request_irq(adapter->pdev->irq, handler, irq_flags, netdev->name, netdev); ... return err; }
当网卡产生数据中断后,调用中断处理函数: 对于napi来说,首先要禁止当前网卡的中断,如果当前没有在运行的napi任务,则调度一个新的napi任务__napi_schedule:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 static irqreturn_t e1000_intr (int irq, void *data) { ... ew32(IMC, ~0 ); E1000_WRITE_FLUSH(); if (likely(napi_schedule_prep(&adapter->napi))) { adapter->total_tx_bytes = 0 ; adapter->total_tx_packets = 0 ; adapter->total_rx_bytes = 0 ; adapter->total_rx_packets = 0 ; __napi_schedule(&adapter->napi); } else { if (!test_bit(__E1000_DOWN, &adapter->flags)) e1000_irq_enable(adapter); } return IRQ_HANDLED; }
启动napi任务,发送软中断 __napi_schedule在/kernel/net/core/dev.c中,其实际做了两件事:
将napi_struct添加到中断处理CPU的softnet_data对应的poll列表中
发出一个NET_RX_SOFTIRQ的软中断,让内核线程ksoftirqd来处理对应的该softirq软中断
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 void __napi_schedule(struct napi_struct *n){ unsigned long flags; local_irq_save(flags); ____napi_schedule(this_cpu_ptr(&softnet_data), n); local_irq_restore(flags); } static inline void ____napi_schedule(struct softnet_data *sd, struct napi_struct *napi) { list_add_tail(&napi->poll_list, &sd->poll_list); __raise_softirq_irqoff(NET_RX_SOFTIRQ); }
__raise_softirq_irqoff函数在/kernel/softirq.c中定义,其作用就是将当前CPU对应的softirq状态标记为待运行状态:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 void __raise_softirq_irqoff(unsigned int nr){ trace_softirq_raise(nr); or_softirq_pending(1UL << nr); }
处理网络软中断 内核在初始化的时候,每个CPU上都会启动一个专门的ksoftirqd%d(%d对应CPU的ID)内核线程用于处理CPU上的软中断(代码同样在softirq.c)中:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 static struct smp_hotplug_thread softirq_threads = .store = &ksoftirqd, .thread_should_run = ksoftirqd_should_run, .thread_fn = run_ksoftirqd, .thread_comm = "ksoftirqd/%u" , }; static __init int spawn_ksoftirqd (void ) { register_cpu_notifier(&cpu_nfb); BUG_ON(smpboot_register_percpu_thread(&softirq_threads)); return 0 ; } early_initcall(spawn_ksoftirqd);
每个内核线程ksoftirqd实际一直执行的是run_ksoftirqd函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 static void run_ksoftirqd (unsigned int cpu) { local_irq_disable(); if (local_softirq_pending()) { __do_softirq(); local_irq_enable(); cond_resched_rcu_qs(); return ; } local_irq_enable(); }
函数__do_softirq检查当前CPU所有待处理的软中断,并调用对应的处理函数softirq_action:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 asmlinkage __visible void __softirq_entry __do_softirq(void ) { ... while ((softirq_bit = ffs(pending))) { unsigned int vec_nr; int prev_count; h += softirq_bit - 1 ; vec_nr = h - softirq_vec; ... h->action(h); ... h++; pending >>= softirq_bit; } ... }
而softirq_action实际是在网络模块初始化的时候注册的(查看/kernel/net/dev.c)中的函数net_dev_init,通过调用open_softirq告知内核启动网络数据传输的两个软中断:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 static int __init net_dev_init (void ) { ... if (register_pernet_subsys(&netdev_net_ops)) goto out; for_each_possible_cpu(i) { struct softnet_data *sd = skb_queue_head_init(&sd->input_pkt_queue); skb_queue_head_init(&sd->process_queue); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&sd->poll_list); sd->output_queue_tailp = &sd->output_queue; #ifdef CONFIG_RPS sd->csd.func = rps_trigger_softirq; sd->csd.info = sd; sd->cpu = i; #endif sd->backlog.poll = process_backlog; sd->backlog.weight = weight_p; } ... open_softirq(NET_TX_SOFTIRQ, net_tx_action); open_softirq(NET_RX_SOFTIRQ, net_rx_action); hotcpu_notifier(dev_cpu_callback, 0 ); dst_subsys_init(); rc = 0 ; }
也就说h->action 调用的实际是net_rx_action函数: 检查当前CPU的softnet_data的poll_list, 取出第一个设备的napi列表, 调用napi_poll获取对应网卡上的数据包,每个设备执行poll会受到两个参数的约束(确保不会占用过多的CPU资源):
netdev_budget_usecs: 每个设备能够处理的最大时间长度(默认是2000us)netdev_budget: 单个设备一次能处理的最大包的配额(默认是300)
一旦超过给定的时间限制或者处理的包达到配额上限, 则直接退出;如果当前poll_list不为空, 则再次触发一个软中断.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 static void net_rx_action (struct softirq_action *h) { struct softnet_data *sd = unsigned long time_limit = jiffies + usecs_to_jiffies(netdev_budget_usecs); int budget = netdev_budget; LIST_HEAD(list ); LIST_HEAD(repoll); local_irq_disable(); list_splice_init(&sd->poll_list, &list ); local_irq_enable(); for (;;) { struct napi_struct *n ; if (list_empty(&list )) { if (!sd_has_rps_ipi_waiting(sd) && list_empty(&repoll)) return ; break ; } n = list_first_entry(&list , struct napi_struct, poll_list); budget -= napi_poll(n, &repoll); if (unlikely(budget <= 0 || time_after_eq(jiffies, time_limit))) { sd->time_squeeze++; break ; } } local_irq_disable(); list_splice_tail_init(&sd->poll_list, &list ); list_splice_tail(&repoll, &list ); list_splice(&list , &sd->poll_list); if (!list_empty(&sd->poll_list)) __raise_softirq_irqoff(NET_RX_SOFTIRQ); net_rps_action_and_irq_enable(sd); }
而napi_poll则调用最初网卡驱动注册的poll函数e1000_clean:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 static int napi_poll (struct napi_struct *n, struct list_head *repoll) { void *have; int work, weight; list_del_init(&n->poll_list); have = netpoll_poll_lock(n); weight = n->weight; work = 0 ; if (test_bit(NAPI_STATE_SCHED, &n->state)) { struct softnet_data *sd = sd->current_napi = n; work = n->poll(n, weight); trace_napi_poll(n); } ... return work; }
函数e1000_clean调用clean_rx从网卡的DMA区域取出数据, 如果处理完成, 则重新开启设备中断:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 static int e1000_clean (struct napi_struct *napi, int budget) { struct e1000_adapter *adapter =struct e1000_adapter, napi); int tx_clean_complete = 0 , work_done = 0 ; tx_clean_complete = e1000_clean_tx_irq(adapter, &adapter->tx_ring[0 ]); adapter->clean_rx(adapter, &adapter->rx_ring[0 ], &work_done, budget); if (!tx_clean_complete) work_done = budget; if (work_done < budget) { if (likely(adapter->itr_setting & 3 )) e1000_set_itr(adapter); napi_complete_done(napi, work_done); if (!test_bit(__E1000_DOWN, &adapter->flags)) e1000_irq_enable(adapter); } return work_done; }
将skb_buff 发送给协议栈 e1000_clean_rx_irq不断的从网卡基于DMA地址从对应的内存环形缓冲区中获取网络数据包,并将数据包以sk_buff的形式传给协议栈进行处理. 简单来说, DMA地址就是外设(网卡)映射到内存的一个虚拟地址, 用于直接与内存(RAM)之间传送数据. 一般在驱动初始化的时候, 网卡通过dma_map_single为缓冲区的每个描述结构体中的数据映射到某个DMA地址, 网卡会把数据拷贝到该DMA地址;CPU收到中断后则数据交由CPU处理, 再通过dma_unmap_single清除掉这个DMA映射.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 static bool e1000_clean_rx_irq (struct e1000_adapter *adapter, struct e1000_rx_ring *rx_ring, int *work_done, int work_to_do) { struct net_device *netdev = struct pci_dev *pdev = struct e1000_rx_desc *rx_desc , *next_rxd ; struct e1000_rx_buffer *buffer_info , *next_buffer ; u32 length; unsigned int i; int cleaned_count = 0 ; bool cleaned = false ; unsigned int total_rx_bytes=0 , total_rx_packets=0 ; i = rx_ring->next_to_clean; rx_desc = E1000_RX_DESC(*rx_ring, i); buffer_info = &rx_ring->buffer_info[i]; while (rx_desc->status & E1000_RXD_STAT_DD) { struct sk_buff *skb ; u8 *data; u8 status; if (*work_done >= work_to_do) break ; (*work_done)++; dma_rmb(); status = rx_desc->status; length = le16_to_cpu(rx_desc->length); data = buffer_info->rxbuf.data; prefetch(data); skb = e1000_copybreak(adapter, buffer_info, length, data); if (!skb) { unsigned int frag_len = e1000_frag_len(adapter); skb = build_skb(data - E1000_HEADROOM, frag_len); if (!skb) { adapter->alloc_rx_buff_failed++; break ; } skb_reserve(skb, E1000_HEADROOM); dma_unmap_single(&pdev->dev, buffer_info->dma, adapter->rx_buffer_len, DMA_FROM_DEVICE); buffer_info->dma = 0 ; buffer_info->rxbuf.data = NULL ; } if (++i == rx_ring->count) i = 0 ; next_rxd = E1000_RX_DESC(*rx_ring, i); prefetch(next_rxd); next_buffer = &rx_ring->buffer_info[i]; cleaned = true ; cleaned_count++; if (unlikely(!(status & E1000_RXD_STAT_EOP))) adapter->discarding = true ; if (adapter->discarding) { netdev_dbg(netdev, "Receive packet consumed multiple buffers\n" ); dev_kfree_skb(skb); if (status & E1000_RXD_STAT_EOP) adapter->discarding = false ; goto next_desc; } .... process_skb: total_rx_bytes += (length - 4 ); total_rx_packets++; if (likely(!(netdev->features & NETIF_F_RXFCS))) length -= 4 ; if (buffer_info->rxbuf.data == NULL ) skb_put(skb, length); else skb_trim(skb, length); e1000_rx_checksum(adapter, (u32)(status) | ((u32)(rx_desc->errors) << 24 ), le16_to_cpu(rx_desc->csum), skb); e1000_receive_skb(adapter, status, rx_desc->special, skb); next_desc: rx_desc->status = 0 ; if (unlikely(cleaned_count >= E1000_RX_BUFFER_WRITE)) { adapter->alloc_rx_buf(adapter, rx_ring, cleaned_count); cleaned_count = 0 ; } rx_desc = next_rxd; buffer_info = next_buffer; } rx_ring->next_to_clean = i; cleaned_count = E1000_DESC_UNUSED(rx_ring); if (cleaned_count) adapter->alloc_rx_buf(adapter, rx_ring, cleaned_count); adapter->total_rx_packets += total_rx_packets; adapter->total_rx_bytes += total_rx_bytes; netdev->stats.rx_bytes += total_rx_bytes; netdev->stats.rx_packets += total_rx_packets; return cleaned; }
e1000_receive_skb实际调用napi_gro_receive将数据发送出去:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 static void e1000_receive_skb (struct e1000_adapter *adapter, u8 status, __le16 vlan, struct sk_buff *skb) { skb->protocol = eth_type_trans(skb, adapter->netdev); if (status & E1000_RXD_STAT_VP) { u16 vid = le16_to_cpu(vlan) & E1000_RXD_SPC_VLAN_MASK; __vlan_hwaccel_put_tag(skb, htons(ETH_P_8021Q), vid); } napi_gro_receive(&adapter->napi, skb); }
函数napi_gro_receive首先会尝试通过GRO(Generic Receive Offload)的方式将数据发送出去,如果网卡本身不支持GRO则会直接将数据报传送给上层协议栈(简单来说GRO就是将数据包累积到一定数量后再传给上层,这样一次性的处理多个数据包从而提升效率,可以参考https://lwn.net/Articles/358910/):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 gro_result_t napi_gro_receive (struct napi_struct *napi, struct sk_buff *skb) { trace_napi_gro_receive_entry(skb); skb_gro_reset_offset(skb); return napi_skb_finish(dev_gro_receive(napi, skb), skb); } EXPORT_SYMBOL(napi_gro_receive);
Intel这个网卡没有开启GRO,所以实际dev_gro_receive直接返回了GRO_NORMAL,这样就通过netif_receive_skb_internal处理数据包:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 static gro_result_t napi_skb_finish (gro_result_t ret, struct sk_buff *skb) { switch (ret) { case GRO_NORMAL: if (netif_receive_skb_internal(skb)) ret = GRO_DROP; break ; case GRO_DROP: kfree_skb(skb); break ; case GRO_MERGED_FREE: if (NAPI_GRO_CB(skb)->free == NAPI_GRO_FREE_STOLEN_HEAD) napi_skb_free_stolen_head(skb); else __kfree_skb(skb); break ; case GRO_HELD: case GRO_MERGED: break ; } return ret; }
对于多核系统来说,一般数据传输处理的CPU跟中断处理的CPU是一致的,后来随着网卡速度的提升,如果把网卡的数据都放到一个CPU处理的话,会导致CPU负载过大进而导致数据传输的延迟,因此有人提出了RPS(Receive packet steering , 就是将数据包的处理任务均衡的分配到各个CPU;要支持该特性,需要打开配置CONFIG_RPS, 同时在内核的配置中/sys/class/net/ethx/queues/rx-0/rps_cpus中将需要处理数据包的CPU设置为1, 这样在处理数据的时候就会将数据包先放到各个CPU的数据队列中进行处理。
这里假定该网卡没有配置RPS,接着会调用__netif_receive_skb处理网络数据。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 static int netif_receive_skb_internal (struct sk_buff *skb) { int ret; net_timestamp_check(netdev_tstamp_prequeue, skb); if (skb_defer_rx_timestamp(skb)) return NET_RX_SUCCESS; rcu_read_lock(); #ifdef CONFIG_RPS if (static_key_false(&rps_needed)) { struct rps_dev_flow voidflow , *rflow = int cpu = get_rps_cpu(skb->dev, skb, &rflow); if (cpu >= 0 ) { ret = enqueue_to_backlog(skb, cpu, &rflow->last_qtail); rcu_read_unlock(); return ret; } } #endif ret = __netif_receive_skb(skb); rcu_read_unlock(); return ret; }
__netif_receive_skb实际调用__netif_receive_skb_core处理数据:__netif_receive_skb_core调用内核初始化时注册的协议类型,并调用其回调函数,由相应的协议来处理该数据包
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 static int __netif_receive_skb(struct sk_buff *skb){ int ret; if (sk_memalloc_socks() && skb_pfmemalloc(skb)) { unsigned long pflags = current->flags; current->flags |= PF_MEMALLOC; ret = __netif_receive_skb_core(skb, true ); tsk_restore_flags(current, pflags, PF_MEMALLOC); } else ret = __netif_receive_skb_core(skb, false ); return ret; } static int __netif_receive_skb_core(struct sk_buff *skb, bool pfmemalloc){ struct packet_type *ptype , *pt_prev ; rx_handler_func_t *rx_handler; struct net_device *orig_dev ; bool deliver_exact = false ; int ret = NET_RX_DROP; __be16 type; net_timestamp_check(!netdev_tstamp_prequeue, skb); trace_netif_receive_skb(skb); orig_dev = skb->dev; skb_reset_network_header(skb); if (!skb_transport_header_was_set(skb)) skb_reset_transport_header(skb); skb_reset_mac_len(skb); pt_prev = NULL ; another_round: skb->skb_iif = skb->dev->ifindex; __this_cpu_inc(softnet_data.processed); if (skb->protocol == cpu_to_be16(ETH_P_8021Q) || skb->protocol == cpu_to_be16(ETH_P_8021AD)) { skb = skb_vlan_untag(skb); if (unlikely(!skb)) goto out; } ... list_for_each_entry_rcu(ptype, &ptype_all, list ) { if (pt_prev) ret = deliver_skb(skb, pt_prev, orig_dev); pt_prev = ptype; } list_for_each_entry_rcu(ptype, &skb->dev->ptype_all, list ) { if (pt_prev) ret = deliver_skb(skb, pt_prev, orig_dev); pt_prev = ptype; } skip_taps: #ifdef CONFIG_NET_INGRESS if (static_key_false(&ingress_needed)) { skb = handle_ing(skb, &pt_prev, &ret, orig_dev); if (!skb) goto out; if (nf_ingress(skb, &pt_prev, &ret, orig_dev) < 0 ) goto out; } #endif ... }
回调协议包 struct packet_type注册的回调函数,把sk_buff传给该协议层处理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 static inline int deliver_skb (struct sk_buff *skb, struct packet_type *pt_prev, struct net_device *orig_dev) { if (unlikely(skb_orphan_frags(skb, GFP_ATOMIC))) return -ENOMEM; atomic_inc (&skb->users); return pt_prev->func(skb, skb->dev, pt_prev, orig_dev); }
所有这些 struct packet_type实际都是在内核初始化的时候通过dev_add_pack注册的,有兴趣的可以跟踪下对应的代码逻辑。至此, 数据包从设备物理层L1传输到了链路层L2了,传输完成了第一步.
总的说来, NAPI针对高负载的数据通讯做了优化, 减少了物理中断数量, 同时又兼顾了各个物理设备在传输调度上的公平性.
参考文献